Feedback of conversation status

It can be strange in a face-to-face conversation when simply no more sentences are spoken to the other person and this uncomfortable silence occurs. Did my counterpart understand me correctly? Should I ask him or her again?
Fortunately we do not only communicate with voice, we also can see and feel. This allows us to understand body language. Therefore, such questions as mentioned above can usually be answered easily in a face-to-face conversation, since we can see and understand the facial expressions and emotions from our counterpart.
When communicating with a voice user interface, there is no such thing as body language or facial expressions, unless the voice user interface is anthropomorphic with a human-like appearance, i.e. having a body and a face. Without this appearance, the user has to be notified in a different way if something went wrong or a background process is taking place.
When communicating with a voice user interface, there is no such thing as body language or facial expressions.
Imagine a call or video meeting where you just hear a long silence after you end speaking. This leads to the other party being asked if it is still there. So if only voice feedback is used, the user can only find out after speaking whether the voice user interface has understood the spoken input or not.
On the one hand, this can be achieved by asking the voice interface itself if it understood the spoken input. On the other hand the user has a second option: waiting for feedback from the voice user interface, e.g. “All right, I got you.”.
But that would not be as pleasant as it seems at first glance, as users want to experience natural dialogues – like talking to a real person. So imagine talking to another person, but after each sentence your counterpart would say “understood” or “heard”. That conversation would probably not last long.
Use visual feedback
If possible, always use visual feedback to inform the user. So the user can immediately see if the voice interface is listening. The simplest form of visual feedback is via a screen, but can also be done on screenless devices with visual cues as we know it mostly from physical products (lights, light patterns), which indicate the status with certain light intervals or color variations.

In addition to a physical indicator, there is a good way to display specific information to the user with on-screen messages too.
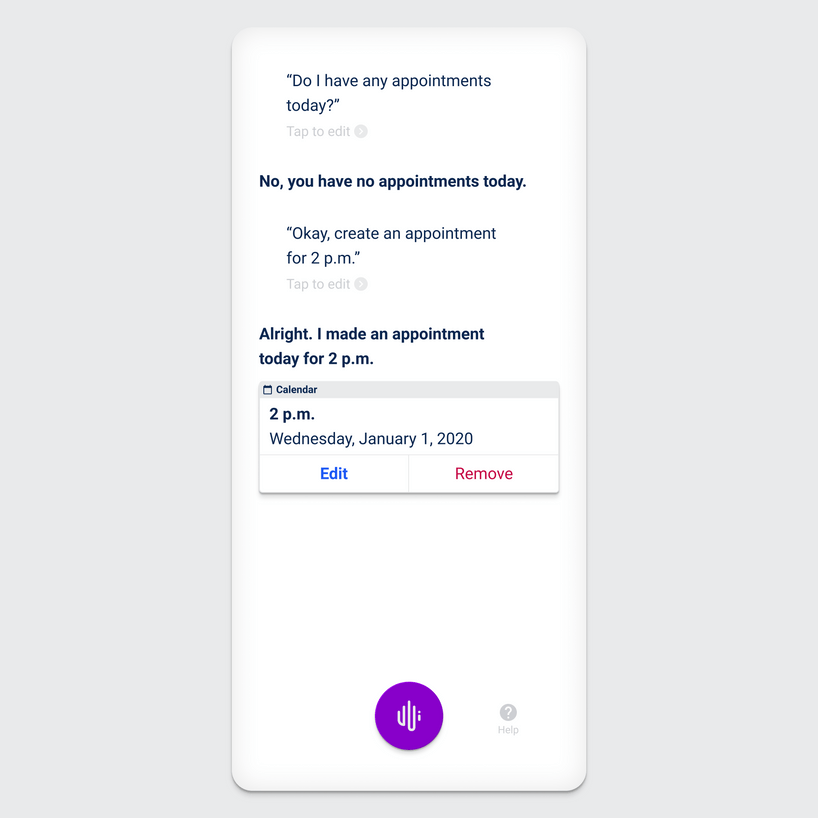
No matter which variant is used, the feedback must be contextual and tell the user what happened. Especially error feedback must show what is wrong and how the user can solve the situation – and not just tell there was an error and showing an unintelligible error code.
In voice user interfaces you want feedback to be brief and to the point, so that it fits to the context. Alone a message with the content “I did not understand you” or “Please repeat” is not optimal, it would be better to provide the error message with specifications as to why the error happened and how the user can prevent the error. For example, “Please speak louder” or “Which model of example name did you mean”?
You can read more about how to implement error messages and prevent errors correctly in the «Prevent and recover from errors» chapter.
Read moreConditions of a voice user interface
In general, we can differentiate between seven conditions that a voice user interface can have:
- Waiting
- Listening
- Thinking
- Replying
- Incomprehension
- Confirmation
- User speaks
Waiting

| Usage | |
|---|---|
| When | In sleep mode or when active, but before the user says an command |
| How | Tell or show the user that the VUI is waiting for inputs, i.e. with possible commands |
Listening

| Usage | |
|---|---|
| When | After the user has said the activation word or in a conversation |
| How | Tell or show the user that he or she can speak and that the VUI is listening |
Thinking

| Usage | |
|---|---|
| When | After the user has said a command |
| How | Tell or show the user that the VUI is processing the user command |
Replying

| Usage | |
|---|---|
| When | After the «Thinking» condition is completed |
| How | Tell or show the user that the VUI is speaking |
Incomprehension

| Usage | |
|---|---|
| When | As soon as any kind of error has happened |
| How | Tell or show the user what exactly occurred the incomprehension and how this can be resolved |
Confirmation

| Usage | |
|---|---|
| When | After the user says an conclusive command |
| How | Tell or show the user that the VUI has understand the command |
User speaks
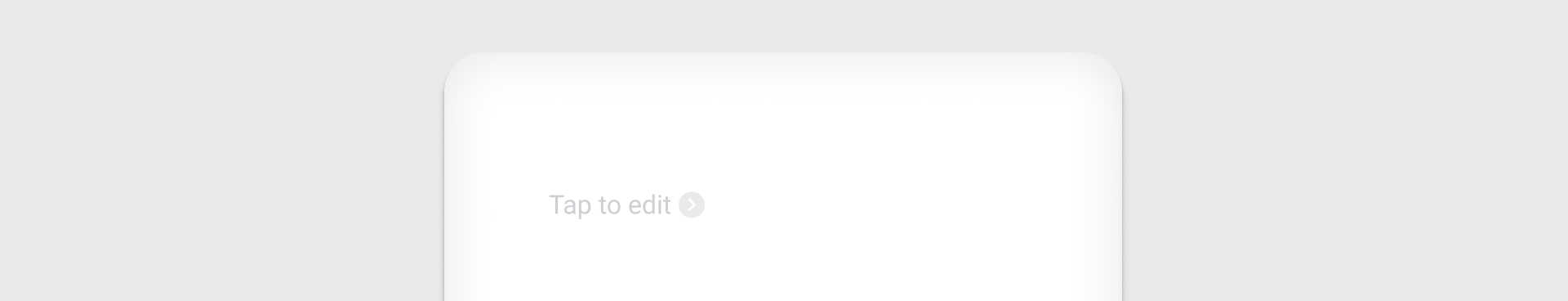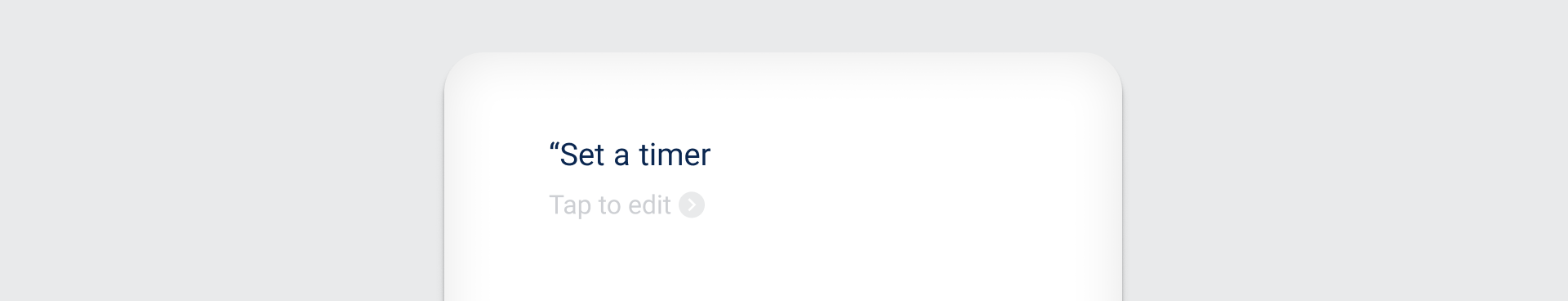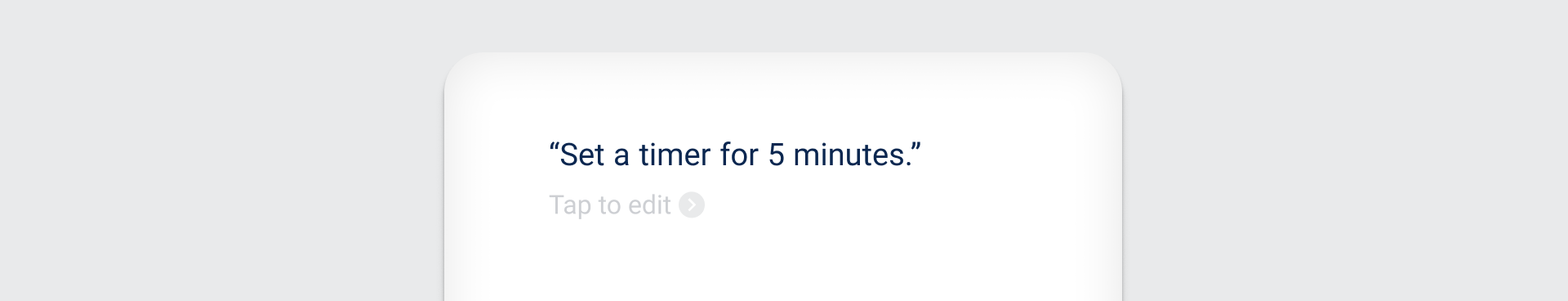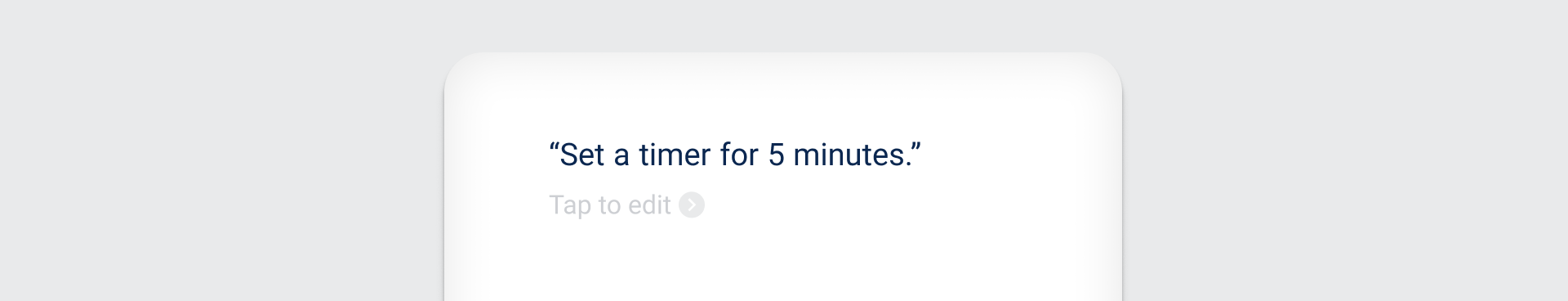
| Usage | |
|---|---|
| When | While the user is speaking |
| How | Show the user that he can speak or that he is speaking |